CE / KS3 Science Bundle - Save 10%!
Buy our CE/KS3 bundle and save 10%!
Revolutionise the way you learn with Oaka Digital
Designed for Dyslexics, Effective for Everyone
Which type of Oaka product do I need?
How Oaka works in the classroom...
Read what other teachers are saying!
Online learning the Oaka way!
Buy our CE/KS3 bundle and save 10%!

Designed for Dyslexics, Effective for Everyone
✅ Learn or revise complicated concepts easily
✅ Information broken down into short chunks
✅ Full-colour illustrations on every page
A great Common Entrance and Key Stage 3 revision guide to remember all those different types of energy, components and their symbols. This guide uses three methods of learning to help increase the long term memory recall, so your child can remember all of the key points they need to know. This revision guide turns a rather tricky topic into a visually interesting one, making concepts easier to understand.
Electric current refers to the flow of electric charge through a material, usually a conductor, and is usually expressed in Amperes (A). Various sources, including batteries, generators, and solar cells can generate electric current. Conductors are materials that allow an electric current to flow easily, while insulators are materials that do not allow electric current to flow easily. Metals such as copper and aluminum are good conductors, while materials such as rubber and glass are good insulators.
Voltage, also known as electric potential difference, measures the electric potential energy per unit charge. The force drives the flow of electric charge through a circuit and is usually measured in volts (V).
Resistance is a measure of the opposition to the flow of electric current in a material. It is a property of materials and is usually measured in ohms (Ω). The greater the resistance of a material, the less electric current will flow through it.
Components in electrical circuits include resistors, capacitors, inductors, diodes and transistors, among others. Each component has a unique symbol that is used to represent it in a circuit diagram. For example, the symbol for a resistor is a zigzag line, the symbol for a capacitor is two parallel lines, and the symbol for an inductor is a spiral.
Stored energy in batteries refers to the energy stored in a chemical form that can be converted into electrical energy as needed. A battery is a device that stores and releases electrical energy by using a chemical reaction to convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy.
Batteries come in many shapes and sizes, and there are many different types of batteries, including primary batteries, which are designed to be used once and then discarded, and secondary batteries, which can be recharged and used multiple times.
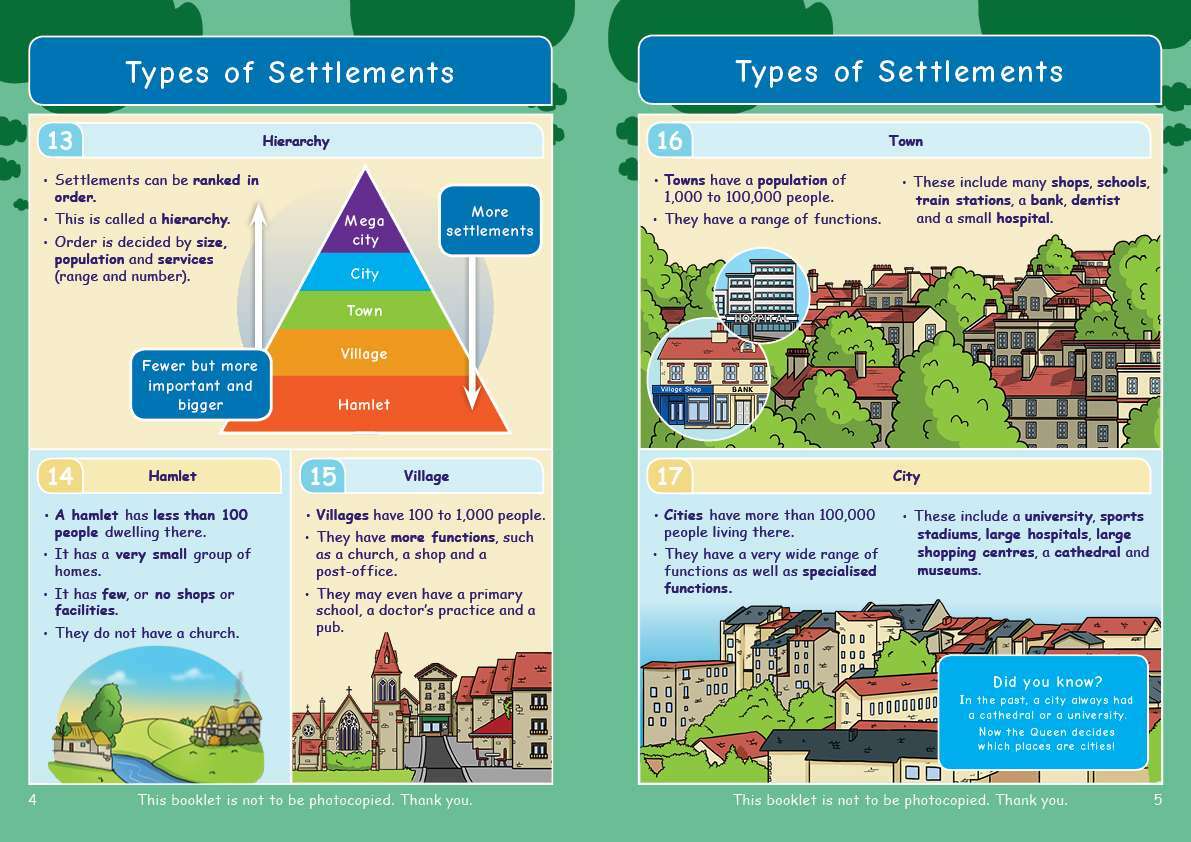
Engaging, full-colour illustrations on every page

Text broken down into bite-sized chunks on a lightly shaded background

A simple, easy-to-understand glossary of key terms
Topic Booklet
Write Your Own Notes Booklet
Active Learning Game or Map
Topic Booklet: ✅ x1
Write Your Own Notes Booklet: ✅ x1
Active Learning Game or Map: ✅ x1
BEST VALUE!
Topic Booklet: ✅ x1
Write Your Own Notes Booklet: ❌
Active Learning Game or Map: ❌
Topic Booklet: ❌
Write Your Own Notes Booklet: ✅ x1
Active Learning Game or Map: ❌
Please note, our resources are NOT to be photocopied. Thank you.
Much more fun than homework, but my child retained so much more info this way.
Full of the right information that covers the important facts that need to be learnt for KS3.
Books are fantastic.
Had a problem- Oaka investigated and sorted a refund.
Great customer service.
5 stars
My son who’s dyslexic thoroughly enjoys using the books, everything about them is very engaging, user friendly and are a great learning tool!!
I absolutely love all the Oaka Books. So straightforward, easy to follow & engaging.
Chemistry
