CE / KS3 Science Bundle - Save 10%!
Buy our CE/KS3 bundle and save 10%!
Revolutionise the way you learn with Oaka Digital
Designed for Dyslexics, Effective for Everyone
Which type of Oaka product do I need?
How Oaka works in the classroom...
Read what other teachers are saying!
Online learning the Oaka way!
Buy our CE/KS3 bundle and save 10%!

Designed for Dyslexics, Effective for Everyone
✅ Learn or revise complicated concepts easily
✅ Information broken down into short chunks
✅ Full-colour illustrations on every page
Light is an essential science concept for your child to understand. This Light Common Entrance and Key Stage 3 topic pack contains all the key points that your child needs to know, using short, concise sentences. Colour illustrations (instead of just standard black text) help your child to stay engaged and interested in the topic they’re learning about. The visualisation of the topic helps make understanding easier.
Light is a type of energy that travels through space in the form of electromagnetic waves. Light is unique in that it behaves both as a particle (photon) and as a wave, a concept known as wave-particle duality.
The speed of light in a vacuum is constant and is the fastest speed at which anything can travel. In other materials, such as air, water, or glass, the speed of light decreases, and the light can be bent or refracted as it passes through the material. Light travels in straight lines and can be described by its wavelength, frequency, and amplitude.
The way light moves through different materials is determined by the material’s refractive index. The refractive index measures the material’s ability to bend light and is defined as the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to the speed of light in the material. Materials with a higher refractive index, such as glass, bend light more than materials with a lower refractive index, such as air.
Light entering a material with a different refractive index changes direction. This bending of light as it passes from one material to another is known as refraction. Refraction is used in many applications, including lenses, which are used to focus light, and prisms, which are used to separate light into its individual colours.
Seeing colours is a complex process that involves the eyes, the brain, and the interpretation of the light that enters the eyes. The colours that we see are a result of the light that is reflected off of objects and enters the eyes.
The eyes contain special cells called cones that are responsible for detecting colours. There are three types of cones in the human eye, each of which responds to different wavelengths of light. These three types of cones allow us to see various colours, from red to green to blue.
When light enters the eye, it passes through the lens and is focused onto the retina, which is located at the back of the eye. The cones in the retina detect the light and send signals to the brain, which interprets the signals and creates the perception of colour.
The interpretation of colour by the brain is also influenced by the background and lighting conditions. For example, the same object may appear differently under different lighting conditions or against different backgrounds. Our KS3 Light resources teach you everything you need to know about the subject, along with visual learning aids.
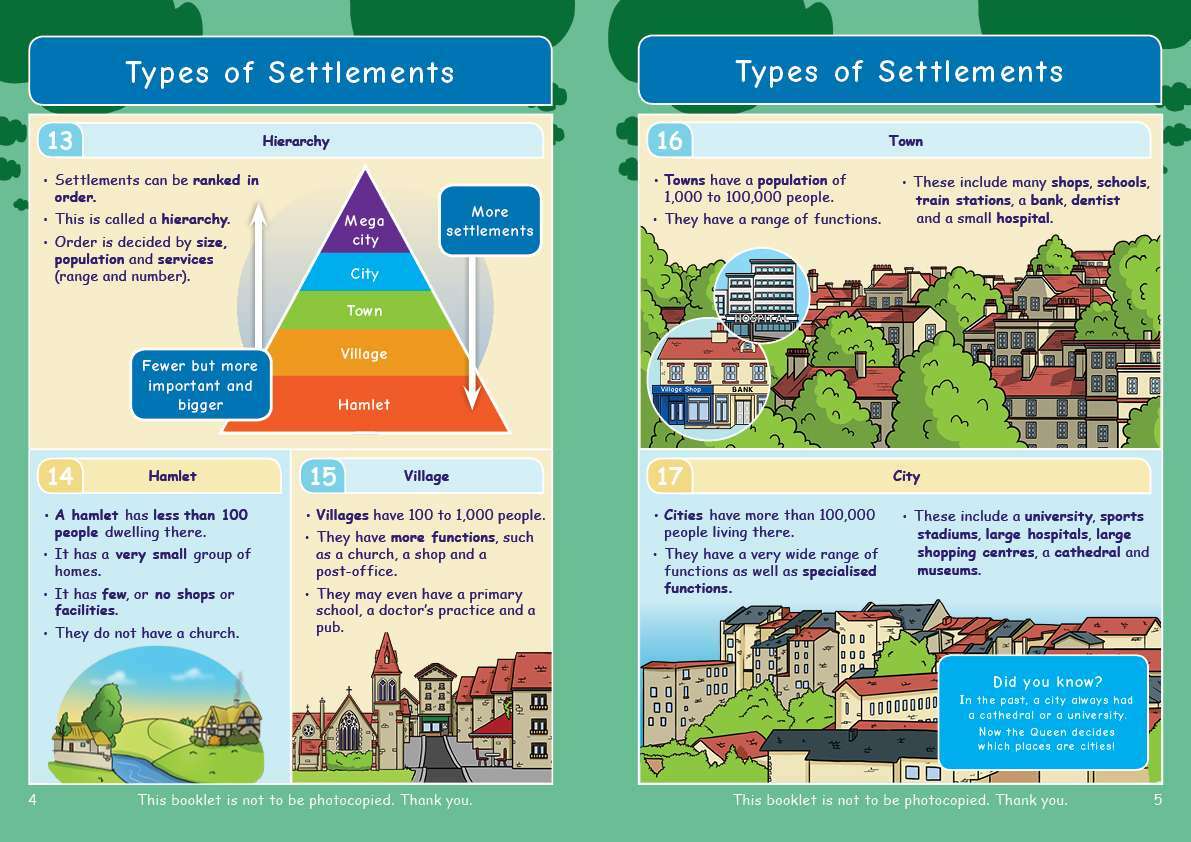
Engaging, full-colour illustrations on every page

Text broken down into bite-sized chunks on a lightly shaded background

A simple, easy-to-understand glossary of key terms
Topic Booklet
Write Your Own Notes Booklet
Active Learning Game or Map
Topic Booklet: ✅ x1
Write Your Own Notes Booklet: ✅ x1
Active Learning Game or Map: ✅ x1
BEST VALUE!
Topic Booklet: ✅ x1
Write Your Own Notes Booklet: ❌
Active Learning Game or Map: ❌
Topic Booklet: ❌
Write Your Own Notes Booklet: ✅ x1
Active Learning Game or Map: ❌
Please note, our resources are NOT to be photocopied. Thank you.
Much more fun than homework, but my child retained so much more info this way.
Full of the right information that covers the important facts that need to be learnt for KS3.
Books are fantastic.
Had a problem- Oaka investigated and sorted a refund.
Great customer service.
5 stars
My son who’s dyslexic thoroughly enjoys using the books, everything about them is very engaging, user friendly and are a great learning tool!!
I absolutely love all the Oaka Books. So straightforward, easy to follow & engaging.
Biology
Physics
Physics
Chemistry
Physics
